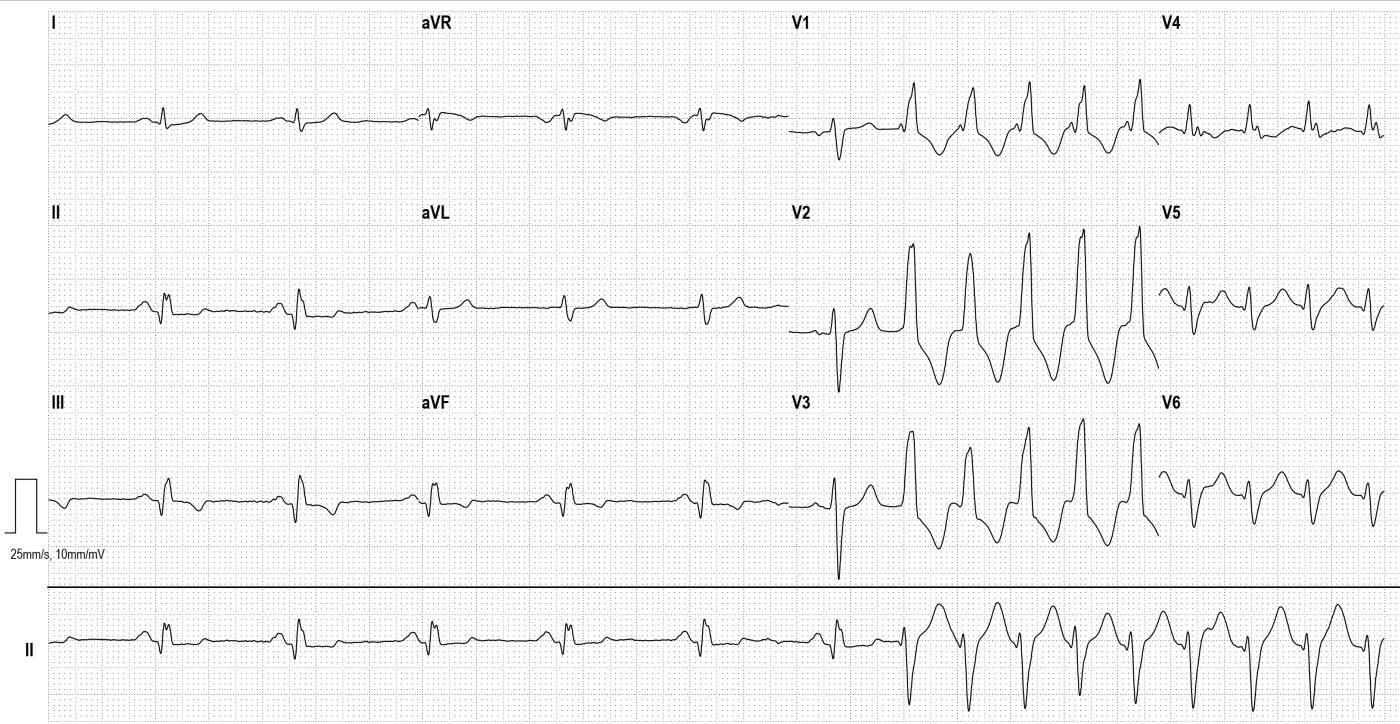
There are several differential diagnoses in the presence of broad-complex tachycardia. The most common cause of wide-complex tachycardia is ventricular tachycardia. In 2nd place is sinus tachycardia/supraventricular tachycardia with aberrant conduction or preexisting bundle branch block.
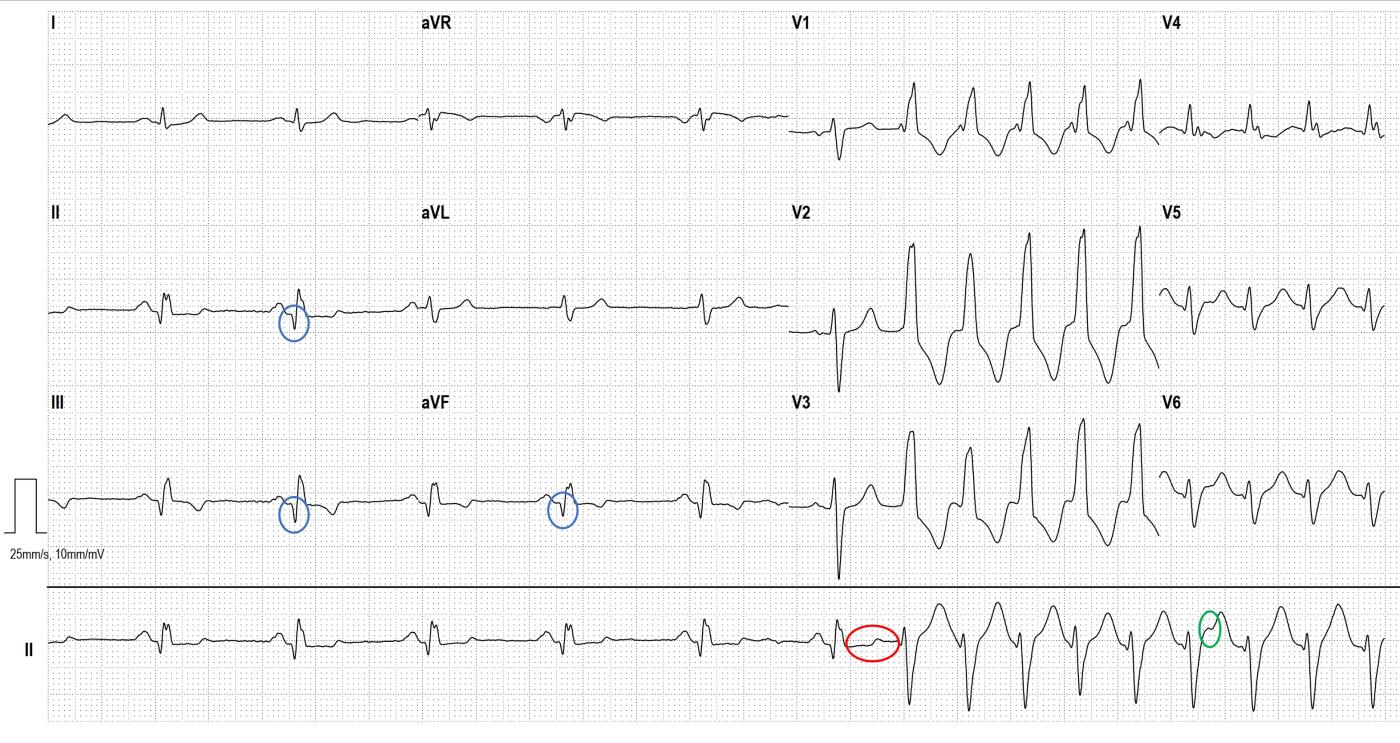
In this case, there are several indications that this is a ventricular tachycardia: If the patient has a history of myocardial infarction, the probability of ventricular tachycardia is about 90%. In this ECG, we can see the pathological Q- waves (circled in blue) in the inferior wall leads, which clearly indicate that a inferior wall infarction has occurred. Furthermore, the tachycardia does not start with a preceding (premature) P wave but with a premature QRS complex (circled in red). The third feature is AV dissociation (fewer P waves than QRS complexes), the only visible P wave during tachycardia is circled in green.
-
- Dr A Röschl's blog
- Log in or register to post comments
All our content is FREE & COPYRIGHT FREE for non-commercial use
Please be courteous and leave any watermark or author attribution on content you reproduce.