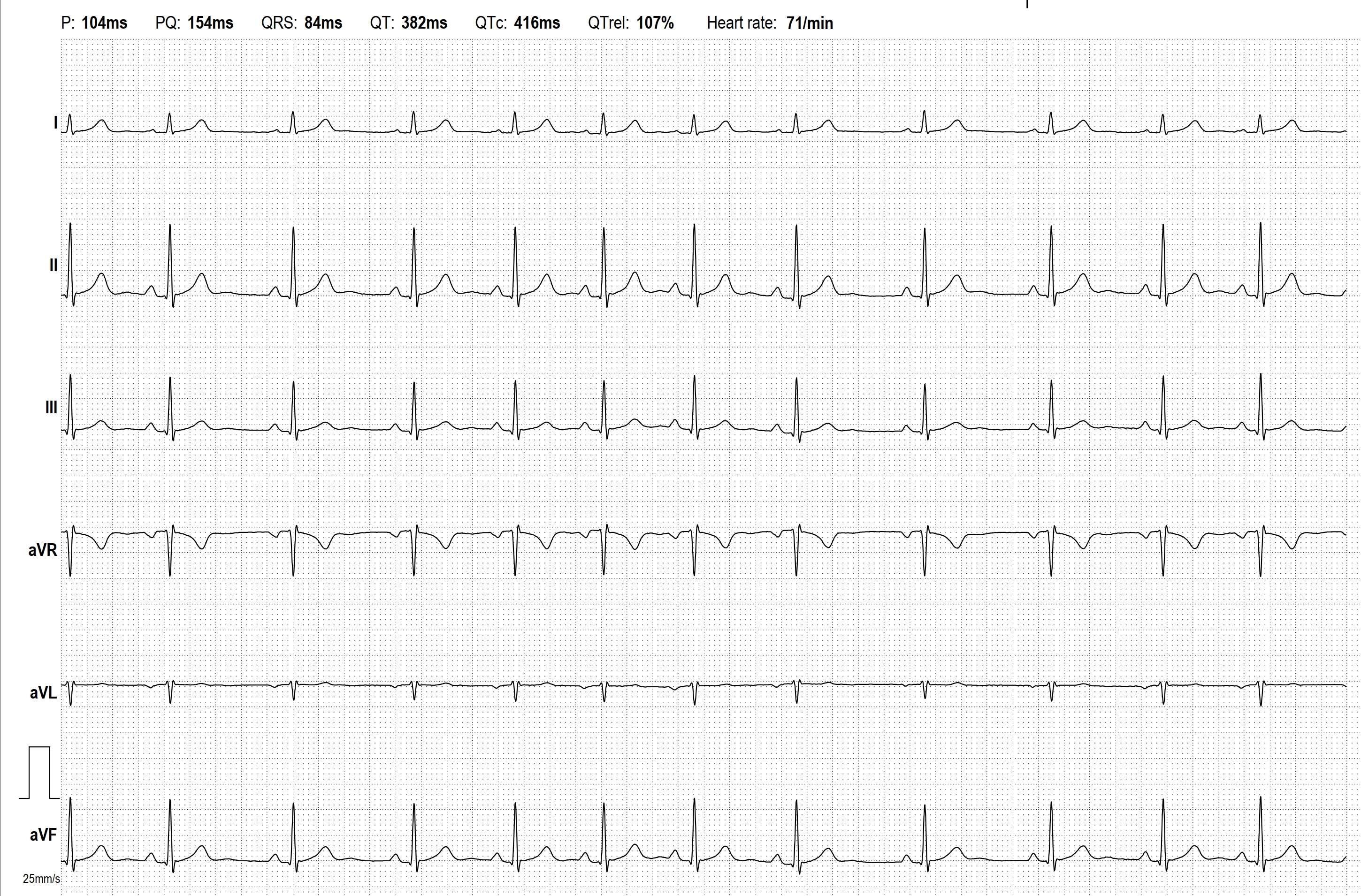
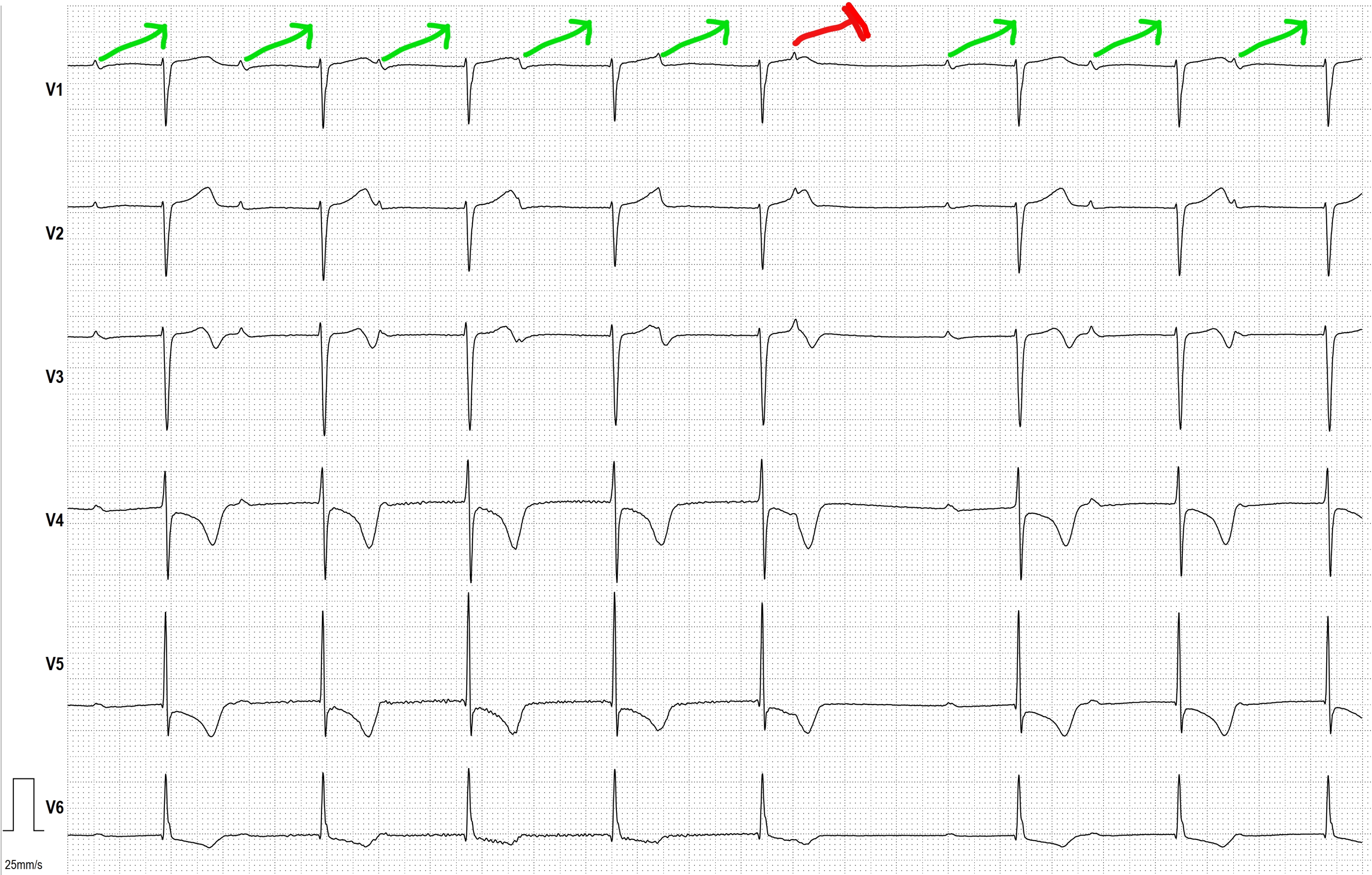
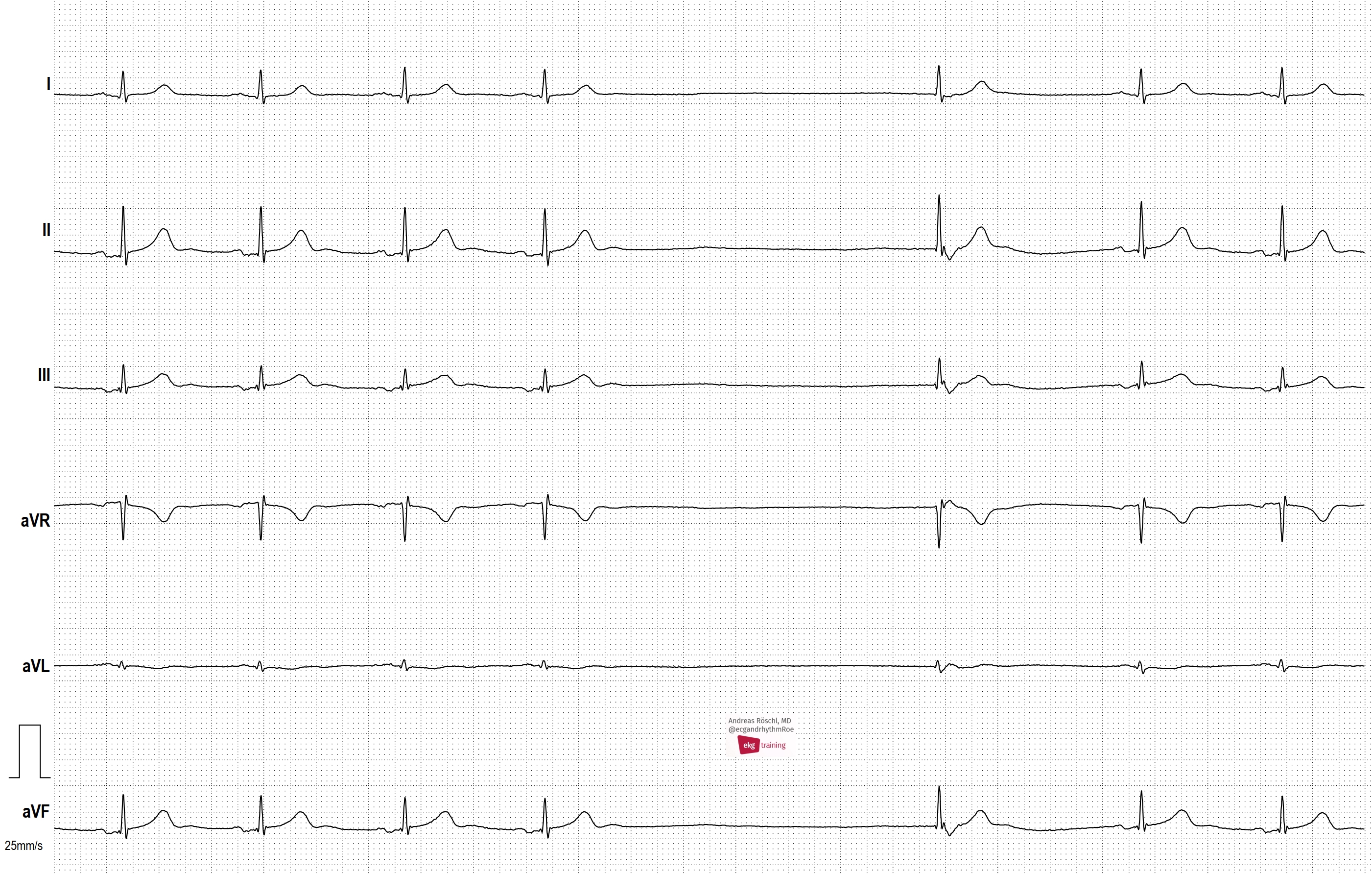
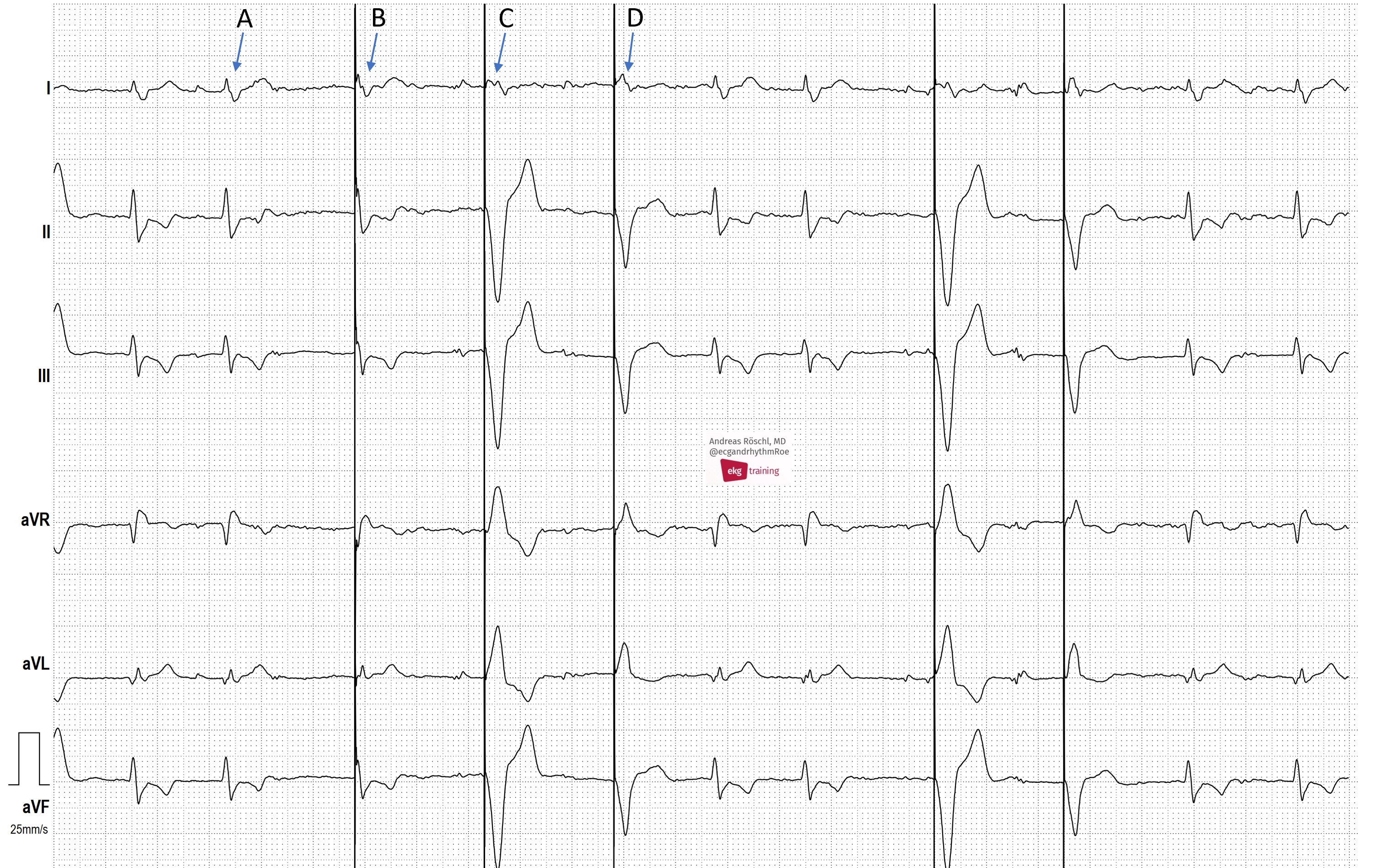
All our content is FREE & COPYRIGHT FREE for non-commercial use
Please be courteous and leave any watermark or author attribution on content you reproduce.
Recent blog posts
- PACS WITH ABERRANT CONDUCTION
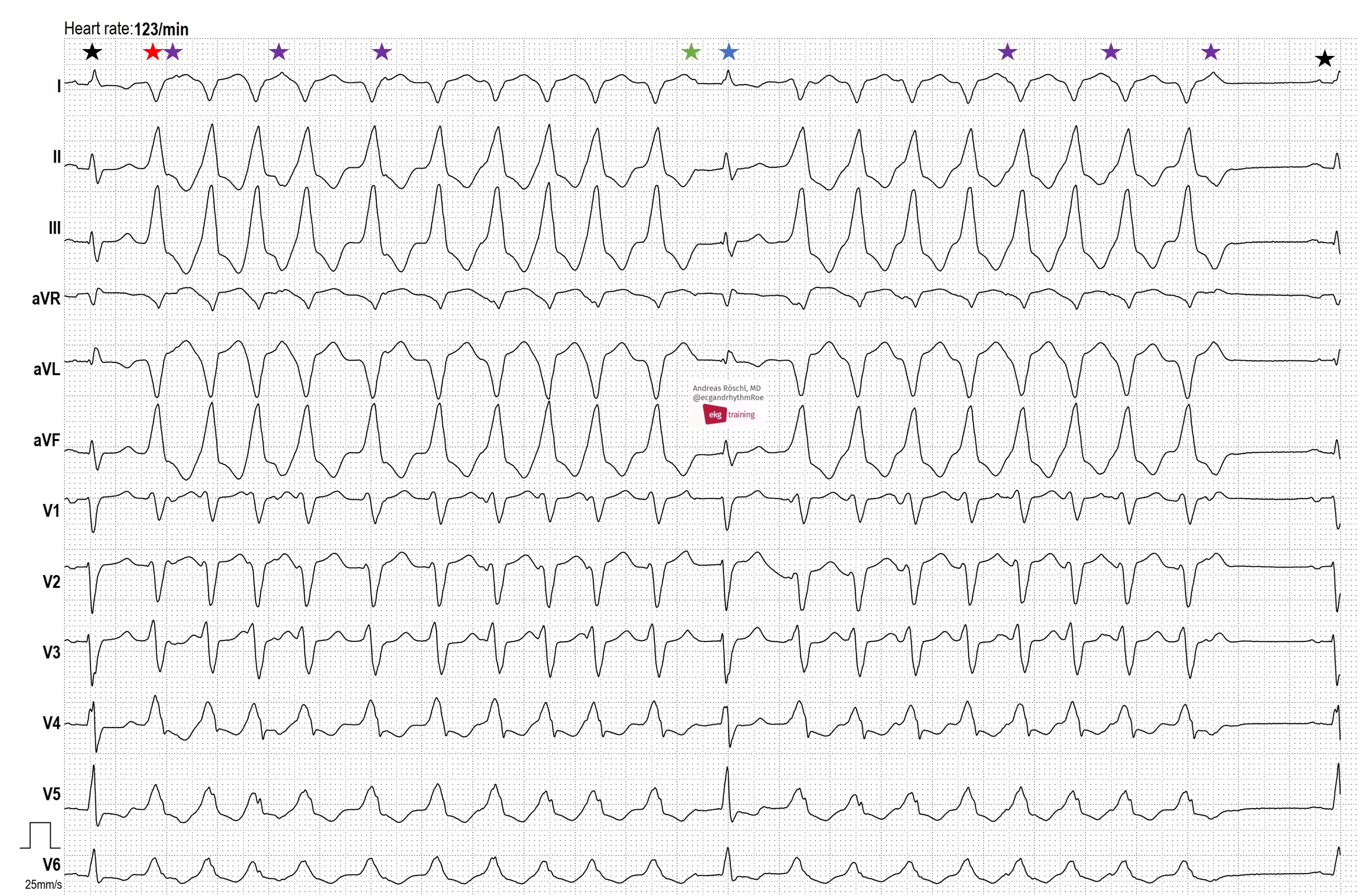
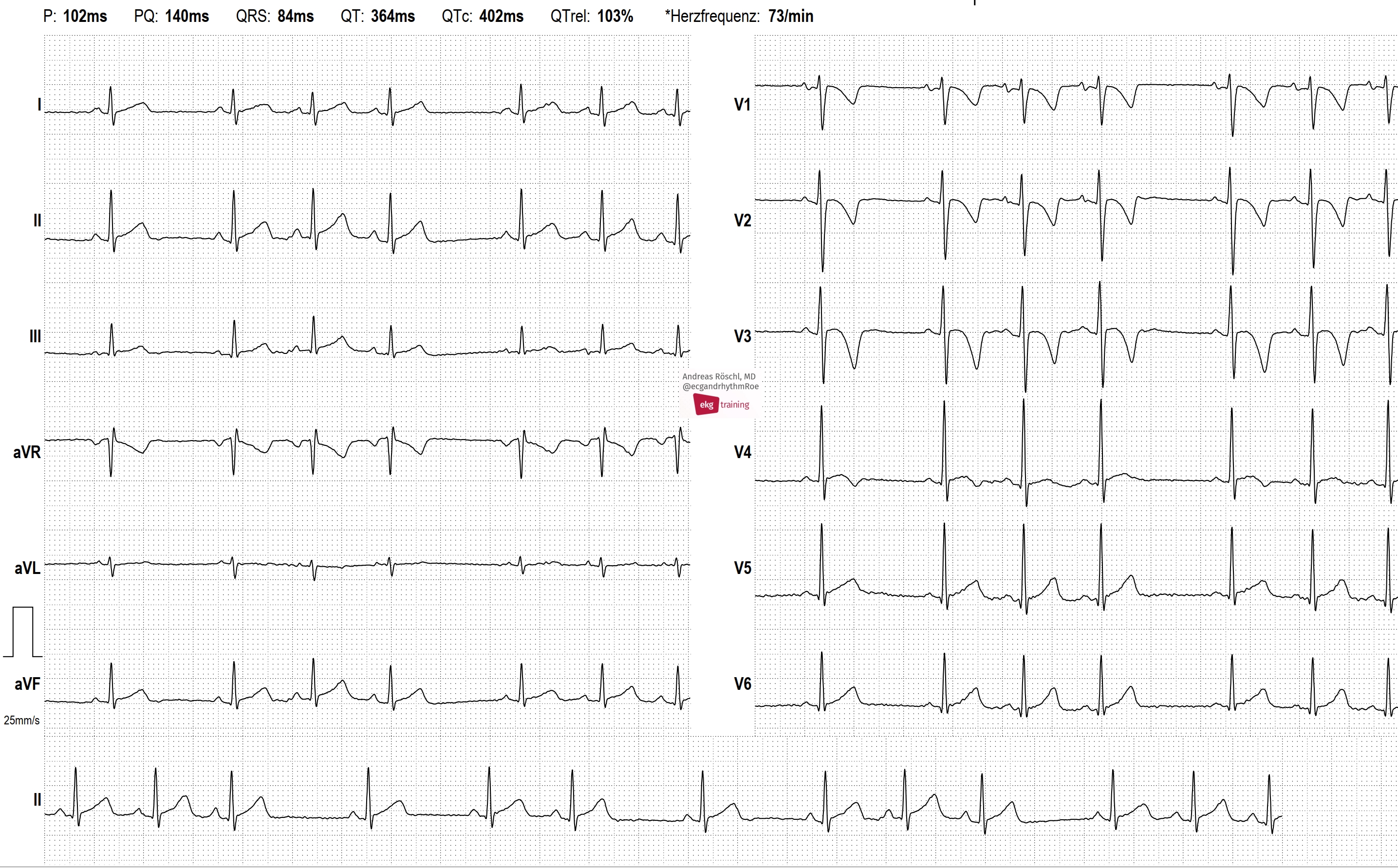
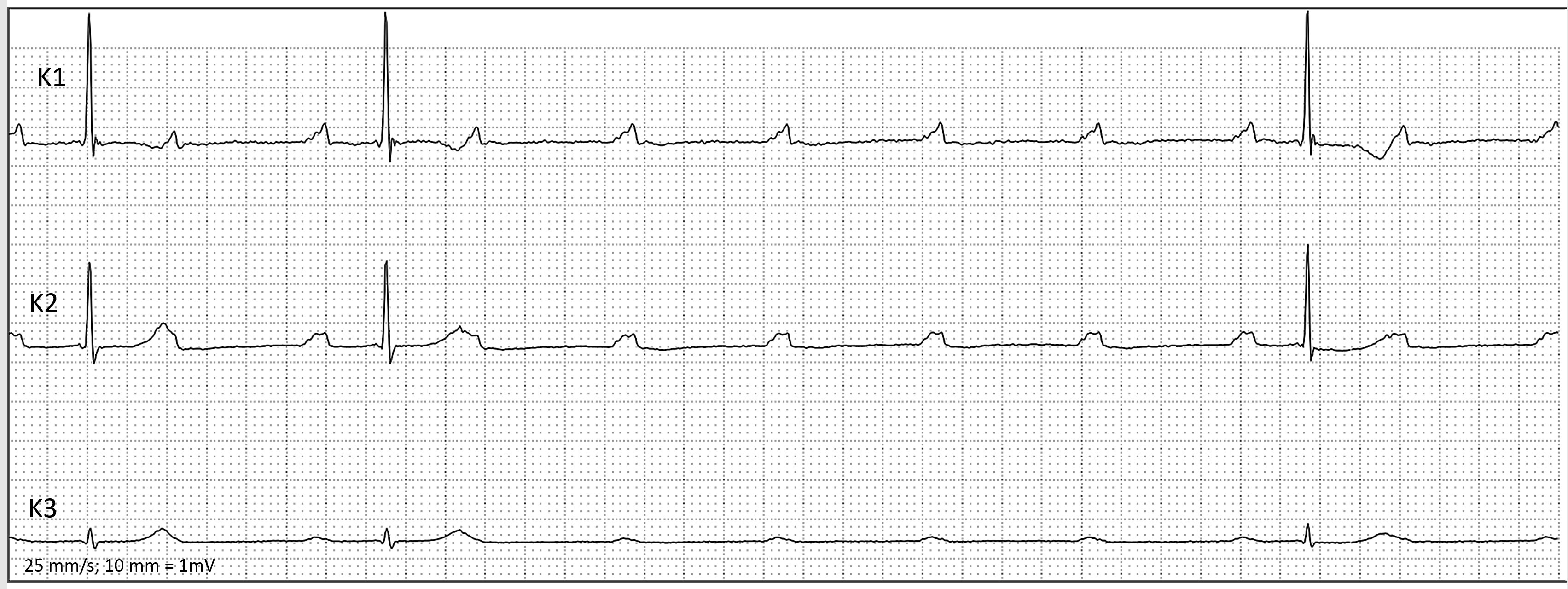
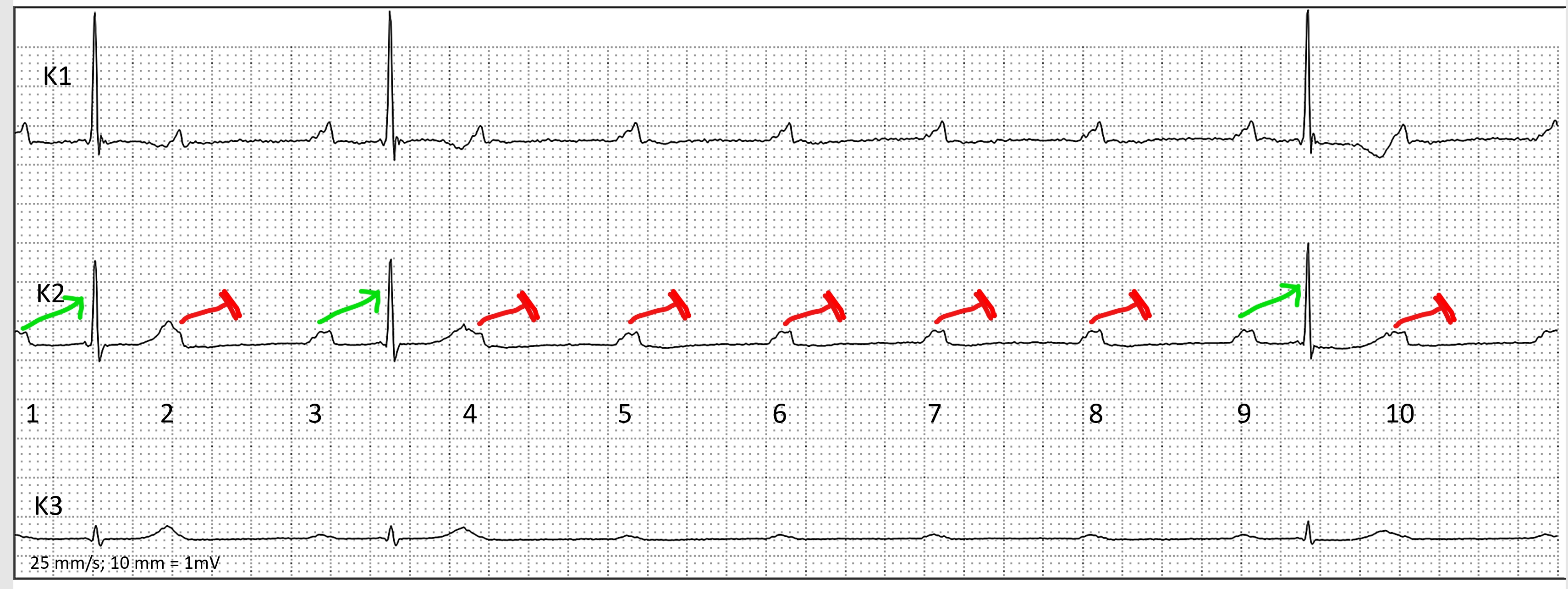
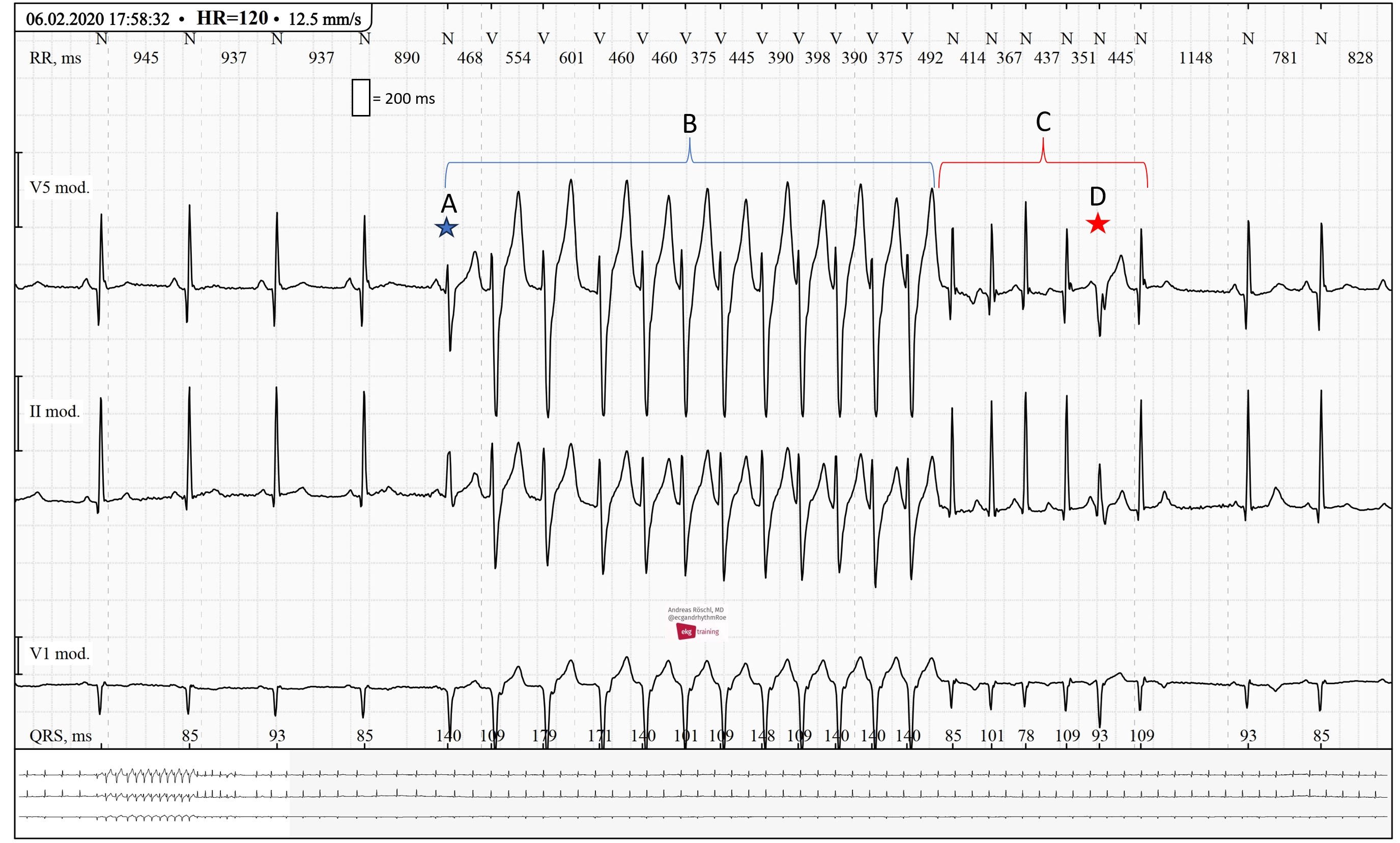
- HOLTER ECG: FAST VT, ATP, ICD SHOCK
- AIVR
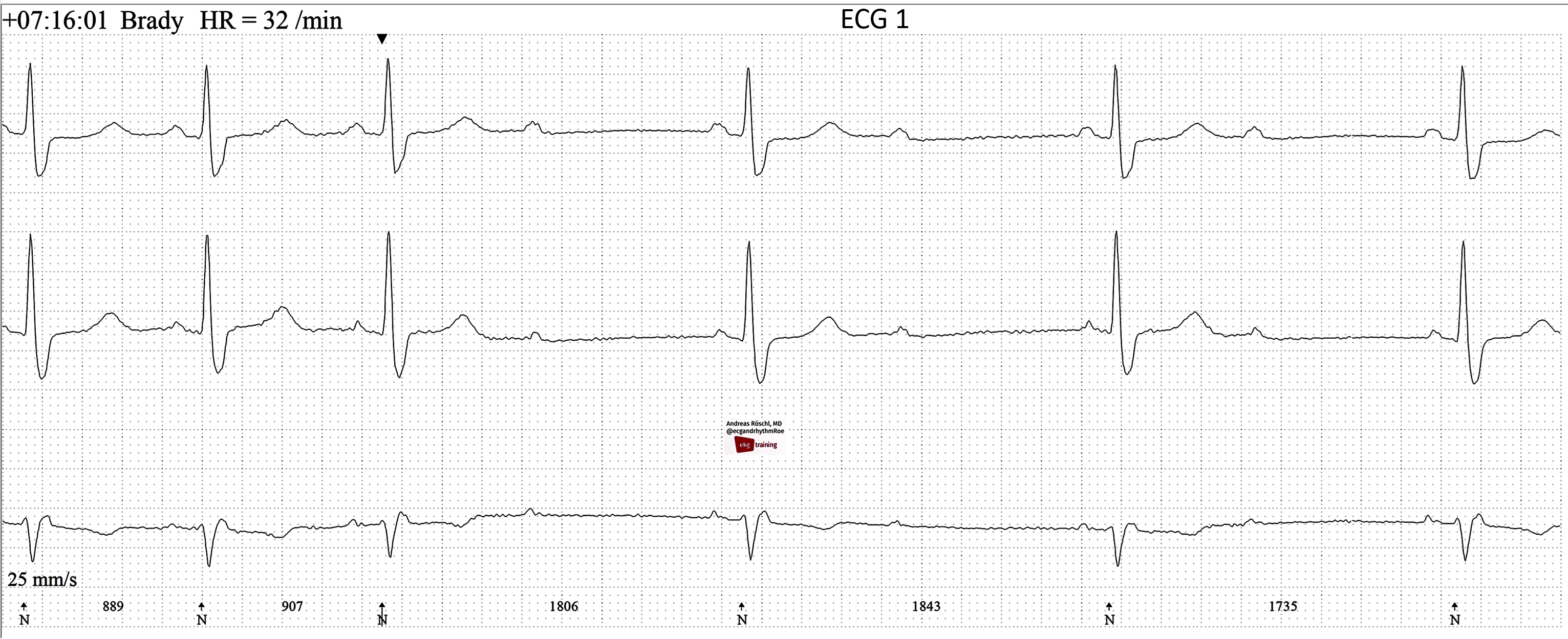
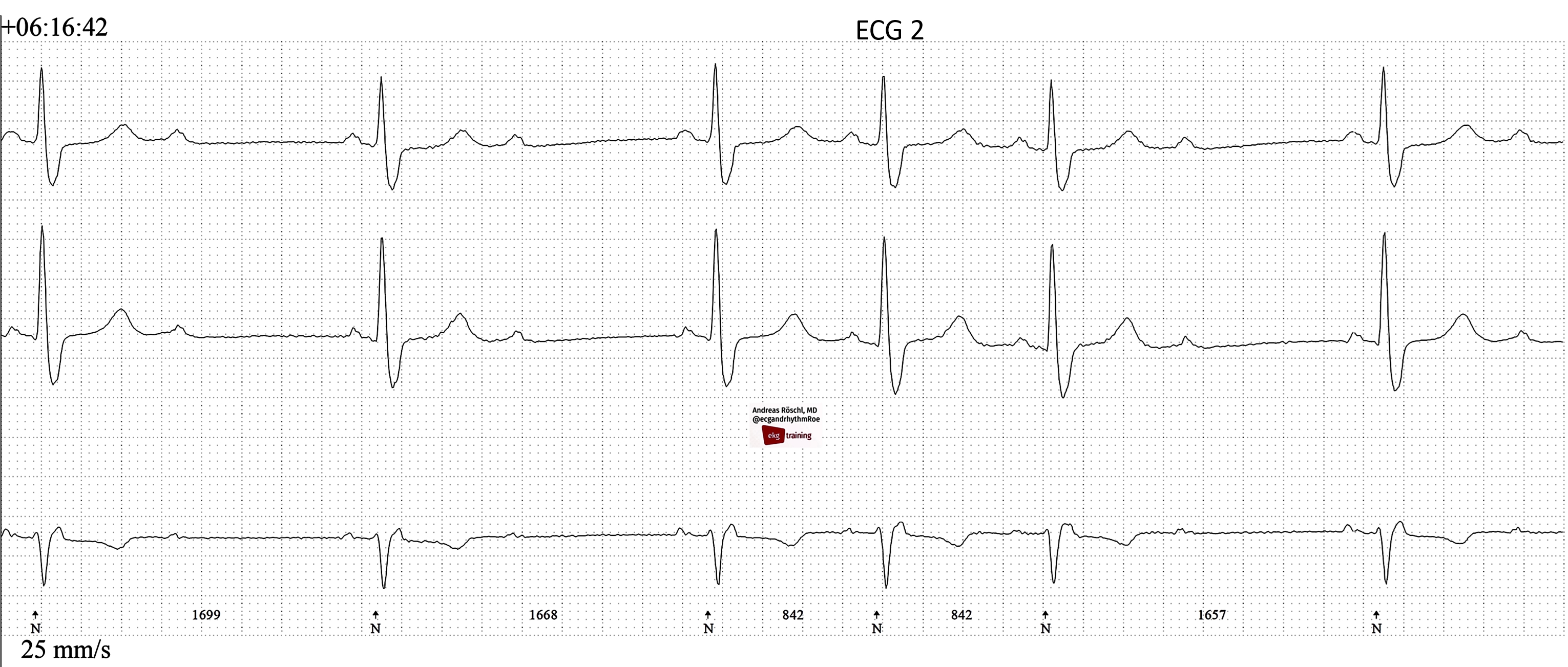
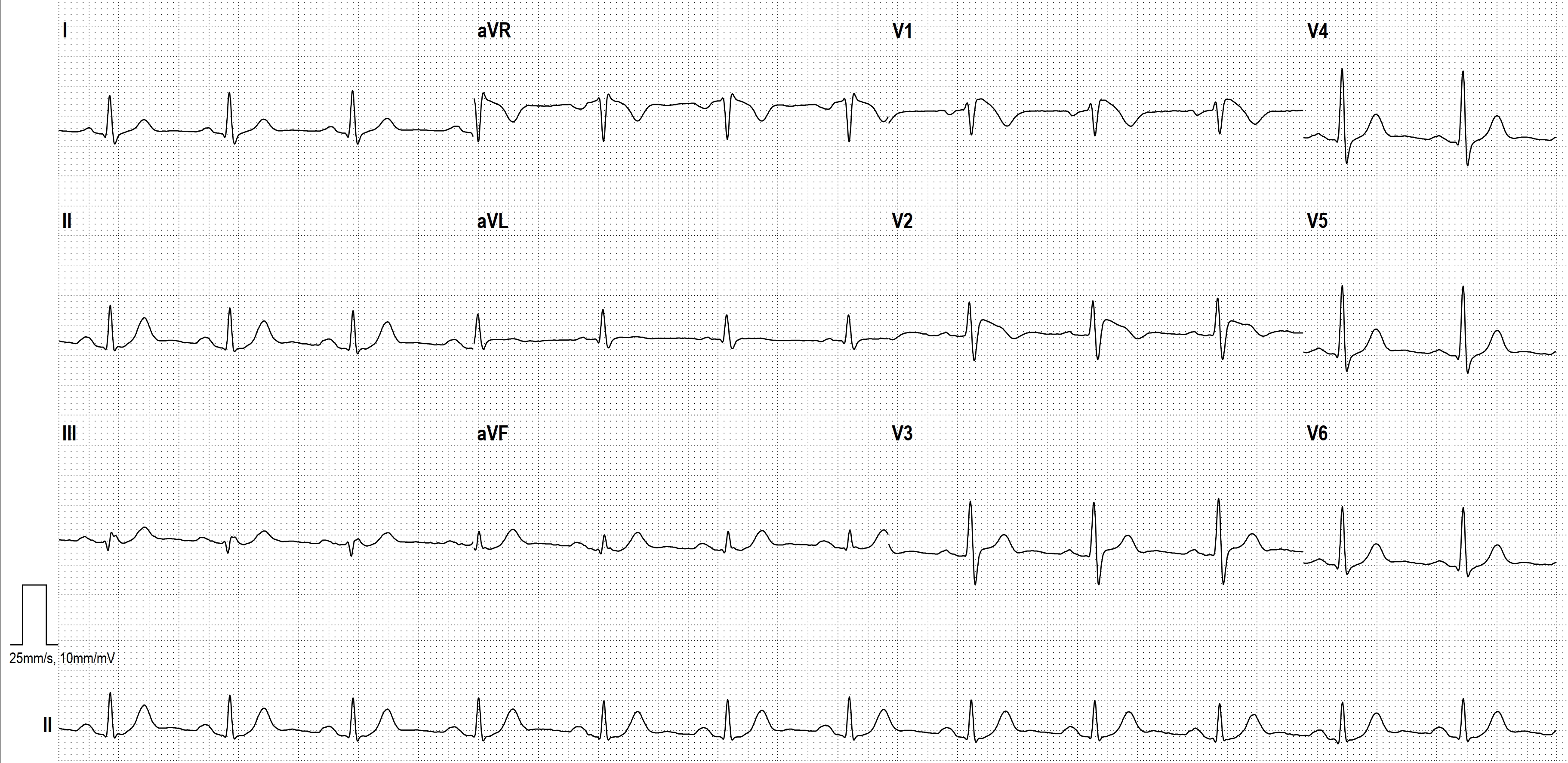
- COMPLETE AV BLOCK
- HIGH GRADE AVB
- JUNCTIONAL ESCAPE RHYTM
- POLYMORPHIC VT
- SGARBOSSA CRITERIA
- CONCEALED CONDUCTION
- CONCEALED CONDUCTION AND VENTRICULOPHASIC SINUS ARRHYTHMIA
- PAROXYSMAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
- 2nd Degree Sino-atrial Exit Block, Mobitz Type II
- SICK-SINUS-SYNDROME
- Smartwatch Rhythm Strip
- NON-CONDUCTED PAC